Until the last time, it has been continued to "Introduction to Software" that presents a program of LEGO Mindstorms, from this time we would like to introduce information related to electricity. This is called "Introduction of Electric". Let's use the wisdom of electricity for making the robots. (Takuya Matsubara)
What is the ultrasonic
"Ultrasonic sensors" is the sensor that measure the distance by using the ultrasound.
It has been adopted officially for the first time for new NXT.
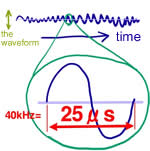
"Ultrasound" is a high-frequency sound. That sound is propagated to the vibration of air. This vibration can be represented as a wave. This is called "frequency" the number of waves that occur per second. Symbol of the unit of frequency is Hz (hertz). And that is called ultrasonic sound of frequency more than 15 kHz generally. Ultrasound could not be heard by the human ear. The ultrasonic sensor in NXT is using the ultrasonic waves of 40 kHz. That is, 40,000 times per second, it is vibrated the air.
Here is the receiver of the contents of the ultrasonic sensor. Ultrasonic sensor has a set of two which are transmit and receive.
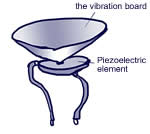
When you figure the structure, it looks like this. Has almost the same structure also send and receive side.
"Piezoelectric element" has interesting characteristics.
If you deform the element, it will produce the electricity. It is called "piezoelectric effect".
On the other hand, adding electricity to element will be transformed into, Referred to as "inverse piezoelectric effect".
You can make, such as sensors and generators by taking advantage of the principle of the piezoelectric effect. You can make the speaker, such as actuators by taking advantage of the principle of the inverse piezoelectric effect.
I tried to create a diagram of the principle of ultrasonic sensors.
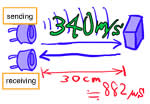
First, the transmitter will raise an ultrasound. When ultrasound is reflected obstacles to return to the receiver. Although the speed of sound varies with temperature approximately 340m / s (meaning they proceed to the second 340 meters 1). For example, if the sound is transmitted time and calculate the distance of 30cm, will be 30 × (1000000 ÷ 34000) =about 882μs. μs (microseconds) is that second 1/1000000. Round-trip time for ultrasonic will be 882 × 2 = 1.764ms. By measuring the time that these small microcomputer, are looking for distance.